Mazda 2: Foreword
Mazda 2 2007-2014 Service Manual / Engine / Foreword
- When the customer reports a vehicle malfunction, check the malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL) indication and
diagnostic trouble code (DTC), then diagnose the malfunction according to
the following flowchart.
- If a DTC exists, diagnose the applicable DTC inspection. (See DTC TABLE ).
- If a DTC does not exist and the MIL does not illuminate or flash, diagnose the applicable symptom troubleshooting. (See QUICK DIAGNOSTIC CHART ).
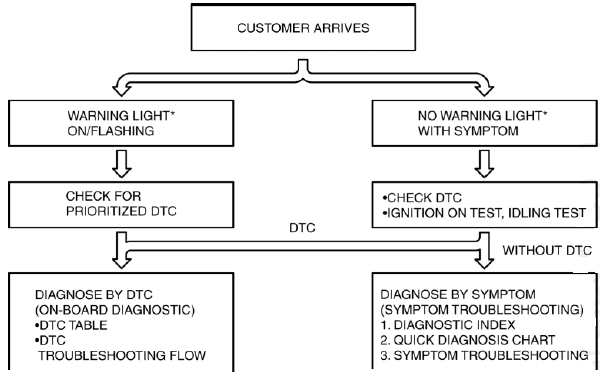
*: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL), Generator Warning Light, Security Light
OBD-II PENDING TROUBLE CODE
- These appear when a problem is detected in a monitored system. The code for a failed system is stored in the PCM memory in the first drive cycle. This code is called the pending code. If the PCM determines that the system has returned to normal or the problem was mistakenly detected, it deletes the pending code. If the problem is found in the second drive cycle, too the PCM determines that the system is malfunctioning, and the DTC is stored.
OBD-II FREEZE FRAME DATA
- This is technical data which indicates the engine condition at the time of the first malfunction. This data will remain in the memory even if another emission-related DTC is stored, with the exception of the Misfire or Fuel System DTCs. Once FREEZE FRAME DATA for the Misfire or Fuel System DTC is stored, it will overwrite any previous data and the FREEZE FRAME DATA will not be overwritten again.
OBD-II ON-BOARD SYSTEM READINESS TEST
- This shows the OBD-II systems operating status. If any monitor function is incomplete, the M-MDS will identify which monitor function has not been completed. Misfires, Fuel System and Comprehensive Components (CCM) are continuous monitoring-type functions. The catalyst, EGR system, evaporation system and oxygen sensor will be monitored under drive cycles. The OBD-II diagnostic system is initialized by performing the DTC cancellation procedure or disconnecting the negative battery cable.
OBD-II READ/CLEAR DIAGNOSTIC TEST RESULTS
- This retrieves all stored DTCs in the PCM and clears the DTC, FREEZE FRAME DATA, On-Board Readiness Test Results, Diagnostic Monitoring Test Results and Pending Trouble Codes.
OBD-II PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION (PID) ACCESS
- The PID mode allows access to certain data values, analog and digital inputs and outputs, calculated values and system status information. Since PID values for output devices are PCM internal data values, inspect each device to identify which output devices are malfunctioning.

